I. Staircase Typology & Spatial Adaptation

1. Straight Stair System
- Spatial requirements: Minimum depth ≥3.5m, bay width ≥0.8m
- Safety performance: Fall risk coefficient 0.12 (lowest among four types)
- Application: Dual-flight design optimizes modern layouts
- Innovation: Integrated storage modules for multifunctional use
2. L-Shaped Stair System
- Space efficiency: 40% improvement over straight stairs
- Golden ratio: Optimal platform dimensions 0.9m×1.2m
- Visual design: Material contrast creates spatial rhythm
- Case study: 89㎡ duplex with bicolor marble mosaic design
3. Curved Stair System
- Minimum radius: 1.8m (ergonomically compliant)
- Craftsmanship: Fan angle per step <5°
- Material innovation: CNC-bent wood/heat-curved glass
- Cost benchmark: ~$350/step (structural reinforcement included)
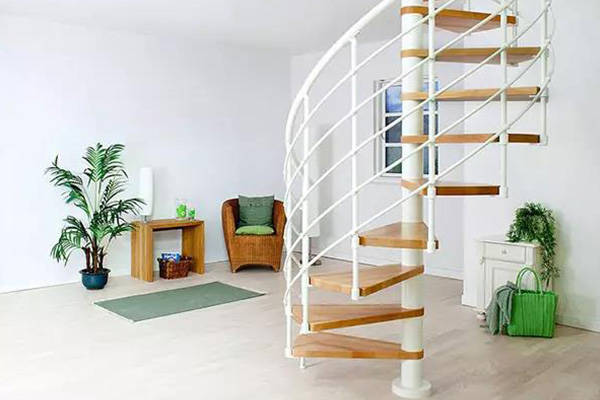
4. Spiral Stair System
- Compact footprint: Central column Ø≥0.3m, total area <1.5㎡
- Safety alert: Tread inner/outer diameter difference >12cm
- Modular solution: Prefabricated steel assembly system
- Restricted use: Prohibited in senior/childcare facilities

II. Ergonomic Design Standards
(Compliant with GB50352-2019 “Unified Standard for Civil Building Design”)
1. Tread Parameter Matrix
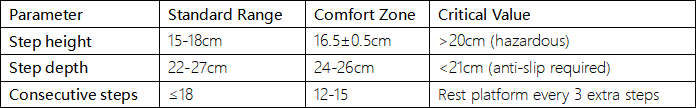
2. Passageway Specifications
- Single user: Clear width ≥75cm (including handrail protrusion)
- Dual traffic: Clear width ≥110cm
- Special cases: 150cm clearance for medical stretchers
3. Safety Guardrails
- Handrail height: 86±2cm from finished floor
- Grip cross-section: Elliptical 5.5cm×3.8mm
- Baluster spacing: ≤11cm (child-proof)
- Load capacity: 1.5kN/m horizontal, 1.0kN/m vertical
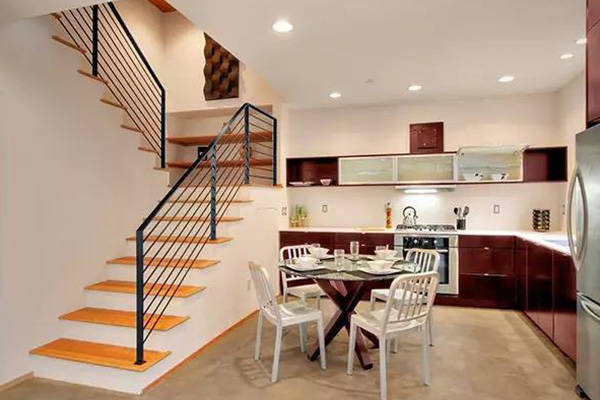

III. Material-Form Compatibility
- Cast-in-place concrete: Best for straight/L-shaped stairs, requires embedded steel frame
- Steel-wood composite: Ideal for spirals, demands dynamic load simulation
- Cantilevered glass: Exclusive to curved stairs, uses 12mm laminated glass
- Stone-clad: Recommended for L-shaped stairs, requires anti-slip treatment
IV. Smart Safety Integration
- Pressure-sensing system: Real-time step load monitoring
- Edge-lit guidance: Auto-dimming LED strips
- Fall-prevention alert: Millimeter-wave motion tracking
- Structural health monitoring: Embedded sensor network
Epilogue
Modern staircase design transcends functional circulation to become spatial art. Prioritize contractors with BIM detailed design capabilities, conduct VR walkthrough simulations during planning, and focus on visual hierarchy at 3rd/15th steps. For complex geometries, engage third-party ANSYS mechanical simulation to ensure vertical deformation ≤L/400. Always verify fire-rated material certifications and acoustic performance parameters for multifamily dwellings.




